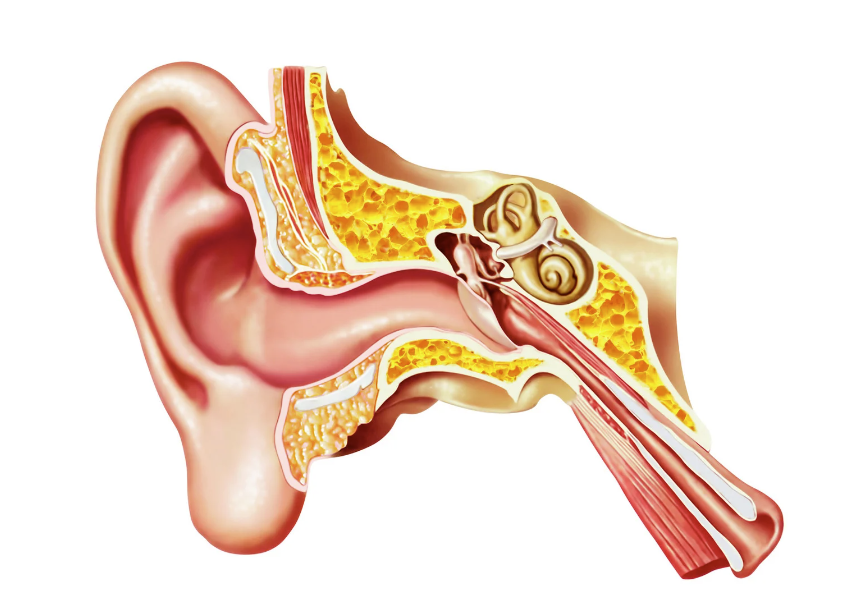
The somatosensory system is crucial for detecting body position and movement through specialized receptors such as mechanoreceptors in muscles, joints, and skin. These receptors, including muscle spindles, Golgi tendon organs, and cutaneous receptors, provide the brain with detailed information about the body's orientation and movement in space. For example, muscle spindles respond to changes in muscle length, helping the body adjust its posture to maintain balance.
Training for Equilibrium: Enhancing Balance and Coordination at Any Age
Introduction: Enhancing Balance and Coordination Through Training
Aging and sedentary lifestyles often lead to significant declines in balance and coordination, which can profoundly impact overall quality of life. These declines increase the risk of falls and injuries, making simple daily activities such as walking, climbing stairs, reaching, and bending more challenging. Deteriorating these skills can heighten the risk of accidents, instill fear of movement, and diminish independence.
Fortunately, targeted training and lifestyle adjustments can significantly improve these essential functions. Training programs designed to enhance balance and coordination can effectively counter the effects of aging and inactivity, fostering a more active, safe, and independent lifestyle.
This article will delve into the importance of balance and coordination, examining how aging and sedentary behavior can impact these abilities. It will also outline practical strategies for improving them through exercise and lifestyle changes. By understanding and addressing these challenges, individuals can boost their physical stability and mobility, leading to a healthier and more vibrant life.

Understanding Balance: The Role of Sensory Systems
Balance is a complex process that relies on the integration of information from the somatosensory, vestibular, and visual systems. These systems collaborate to maintain stability and orientation. Diminishment or impairment in any of these three systems can greatly increase an individual's difficulty in balancing, affecting their overall mobility and safety.
Somatosensory System
Vestibular System
Visual System
Skeletomuscular Impact on Balance and Coordination
The skeletomuscular system, encompassing muscles, joints, and bones, plays a pivotal role in maintaining balance and coordination. Muscle strength, joint flexibility, and skeletal alignment are crucial elements that contribute to stable and coordinated movements.
Muscle Strength
Strong muscles are essential for balance and coordination, providing the power and endurance to maintain posture and initiate movements. As individuals age or lead sedentary lifestyles, muscle mass and strength can decrease, a condition known as sarcopenia. This loss of muscle strength undermines the body's ability to perform basic balance and coordination tasks, increasing the risk of falls and injuries.
Joint Flexibility
Joint flexibility allows for a full range of motion, which is essential for performing complex movements smoothly and efficiently. Adequate joint flexibility facilitates ease of movement and is integral to balance and coordination. With aging and inactivity, joints can become stiff and less mobile, limiting the range of motion and affecting the body's ability to balance and coordinate movements effectively.
Skeletal Alignment
Proper skeletal alignment ensures that the even distribution of the body's weight, allowing optimal balance and efficient movement patterns. Misalignments can lead to uneven weight distribution, placing additional stress on specific muscles and joints and disrupting balance and coordination. Aging and sedentary behavior can exacerbate these misalignments, leading to compensatory movements that further impair balance and coordination.
The combined effects of aging and inactivity on the skeletomuscular system can significantly impact balance and coordination. Loss of muscle strength reduced joint flexibility, and poor skeletal alignment can all contribute to a decline in these critical physical abilities. Therefore, maintaining the health and functionality of the skeletomuscular system is essential for preserving balance and coordination, especially as individuals age or lead inactive lifestyles.

Neuromuscular Control and Balance
Neuromuscular control is essential for executing coordinated movements and maintaining balance, involving the intricate communication between the nervous system and muscles to facilitate precise and efficient movement.
Importance of Neuromuscular Control
Neuromuscular control is the cornerstone of our ability to perform simple and complex movements accurately and efficiently. It involves muscle activation patterns, timing, and force production, which are all vital for maintaining posture, stability, and coordinated motion.
- Muscle Activation Patterns: Neuromuscular control dictates which muscles are activated and in what order to perform a movement. This coordination ensures that movements are smooth and efficient, reduces the risk of overuse injuries, and enhances the ability to perform tasks effectively.
- Timing: The timing of muscle activation is crucial for coordination. Proper neuromuscular control ensures that muscles activate at the right moment to produce fluid and synchronized movements, allowing for actions like walking or jumping to occur naturally and without unnecessary strain.
- Force Production: Neuromuscular control regulates the force muscles produce during movement. This is essential for tasks that require different levels of strength and speed, enabling the body to adjust to varying demands, whether lifting a heavy object or catching a falling glass.
Sedentary Behavior and Neuromuscular Function
Sedentary behavior specifically impacts neuromuscular function by weakening neural connections and diminishing muscle fiber activation, crucial components for maintaining balance and coordination. A lack of physical activity leads to reduced stimulation of the neuromuscular system, which can result in decreased muscle strength and impaired coordination. The decline in proprioceptive feedback in sedentary individuals hampers the body's ability to sense its position and movement in space, making quick and accurate reactions to balance disturbances more challenging.
Regular physical activity challenging the neuromuscular system can significantly enhance balance and coordination. Exercises focusing on strength, flexibility, and proprioception are particularly beneficial in maintaining or improving neuromuscular function, stability, and movement efficiency. Therefore, combatting the effects of a sedentary lifestyle with targeted neuromuscular training is essential for preserving balance and coordination, underscoring the importance of an active lifestyle for optimal neuromuscular health.

Assessing Balance and Coordination
Regular assessment of balance and coordination is crucial for identifying strengths and weaknesses in these areas and developing effective training programs. Standard methods and tests used to evaluate these skills include:
- Berg Balance Scale: A widely used test in clinical settings that assesses static and dynamic balance abilities through various tasks like standing up from a seated position, standing on one foot, and leaning forward.
- Timed Up and Go (TUG) Test: This test measures the time it takes for an individual to rise from a chair, walk a short distance, turn around, walk back to the chair, and sit down. It helps assess mobility, balance, and fall risk.
- Dynamic Gait Index (DGI): Evaluates an individual's ability to modify balance while walking in the presence of external demands, such as changing walking speed, turning the head, or negotiating obstacles.
These assessments are vital in tailoring exercise programs to individual needs, monitoring progress, and adjusting training regimens to optimize balance and coordination outcomes.
Training to Improve Balance and Coordination
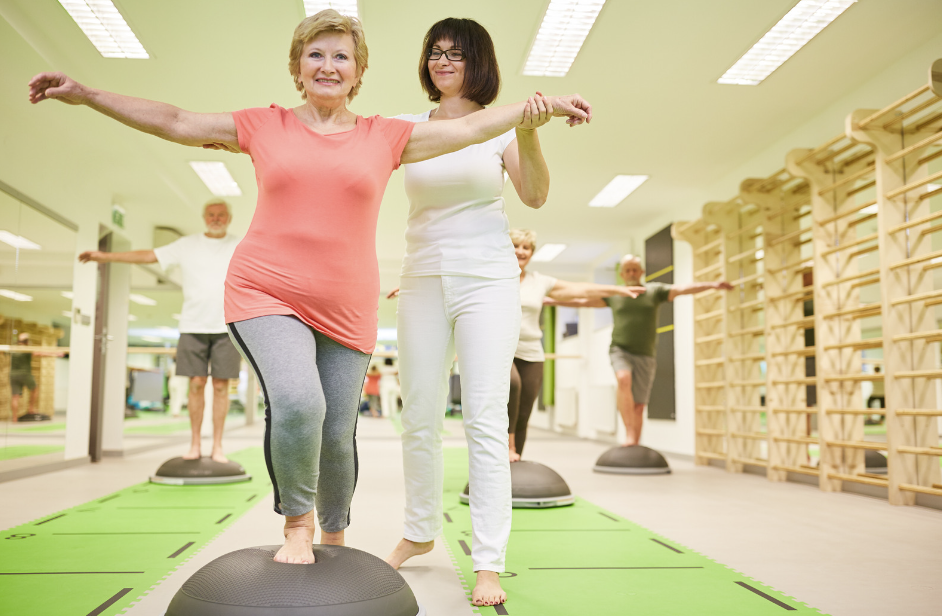

Targeted exercise programs are vital in enhancing balance and coordination. These programs should be multifaceted, incorporating strength training, flexibility exercises, and specific balance and coordination drills. Two prominent methods utilized by certified personal trainers to improve these areas are:
- NASM's Corrective Exercise Continuum (CEC): This methodology involves a four-step process to improve muscular imbalances and altered joint motion. It starts with inhibiting overactive muscles, lengthening tightened structures, activating weak muscles, and integrating dynamic movements to improve balance and coordination.
- ACE Fitness's Integrated Fitness Training (IFT) Model: This approach to exercise programming promotes stability and mobility through customized exercises that enhance functional movement and physical performance.
Examples of exercises to improve balance and coordination might include:
Balance Exercises
- Seated leg lifts and extensions using a chair for support to build leg strength and balance.
- Standing behind a chair, practice rising onto your toes and then gently lifting one foot slightly off the ground, using the chair for support.
- Walking heel-to-toe in a straight line, with a chair or wall nearby for support, improves dynamic balance.
Coordination Exercises
- Ball tosses with a partner to improve hand-eye coordination and reaction time.
- Agility drills like side steps or zig-zag patterns enhance coordination and movement precision.
Strength Exercises
- Squats build lower body strength and improve joint stability, which is fundamental for maintaining balance.
- Lunges with twists engage the core and lower body simultaneously, enhancing strength and coordination.
Including these exercises in regular physical activity routines can significantly improve balance and coordination, contribute to overall physical health, reduce the risk of falls and injuries, and enhance the ability to perform daily activities efficiently and safely.
Royal Blue Fitness: Specialized Support for Enhanced Balance and Coordination
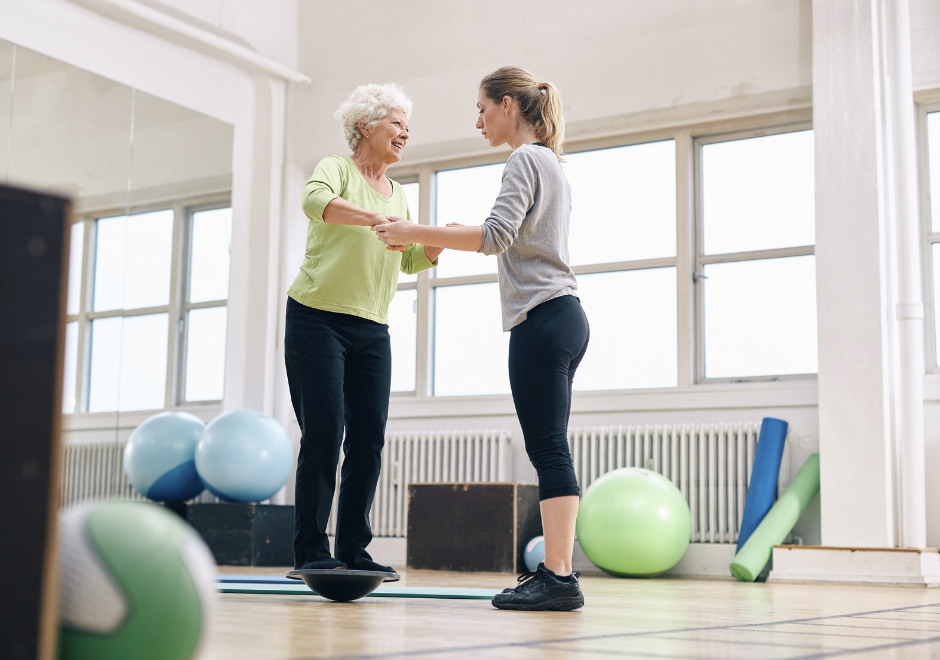

Royal Blue Fitness provides personalized training plans and expert guidance designed to improve balance and coordination, tailored explicitly for aging or sedentary individuals. Our approach starts with a comprehensive assessment to determine each client's unique needs and balance capabilities. Based on this assessment, we develop customized training plans that incorporate balance exercises, coordination drills, and strength training, all aimed at enhancing the individual's ability to maintain and improve balance and coordination.
Our experienced trainers specialize in creating safe and effective workout routines that address each client's specific needs and make the process engaging and enjoyable. Focusing on gradual progression and consistent support, our clients improve their balance and coordination, leading to a more active and independent lifestyle.
Conclusion
Balance and coordination are critical in daily life, especially as we age or lead more sedentary lives. Targeted training programs are essential for improving these vital skills, enhancing overall mobility, and reducing the risk of falls and related injuries. Royal Blue Fitness is the ideal partner in this journey, offering expert-led, personalized training programs specifically designed to enhance balance and coordination.
By choosing Royal Blue Fitness, individuals gain access to the specialized support necessary to maintain and improve their balance and coordination, ensuring a healthier, more active, and independent life.
Resources for Fall Prevention and Balance
For further reading on fall prevention and balance training, the following sources provide reliable information and practical advice based on scientific research:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) - Fall Prevention: Offers comprehensive resources on fall prevention strategies. CDC Fall Prevention
- National Institute on Aging: Provides insights into balance and fall prevention exercises for older adults. National Institute on Aging - Balance
- American Physical Therapy Association (APTA): Features guidelines and tips for balance improvement and fall prevention. APTA Balance and Falls
- Mayo Clinic - Balance Exercises: Includes a guide on simple balance exercises that can be done at home. Mayo Clinic Balance Exercises
These resources offer valuable guidance for individuals looking to improve their balance and coordination, providing a foundation for safer and more effective training programs.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter and posts