Diabetes in Focus: Proactive Steps to Better Health
Introduction: Navigating the Challenges of Diabetes
Diabetes is more than just a health condition; it's a global epidemic that affects millions of lives deeply and diversely. From Type 1, which typically manifests early in life, to Type 2, more commonly developed in adulthood, and gestational diabetes, which occurs during pregnancy—each type poses unique challenges and risks. In the United States alone, over 34 million people have diabetes, and worldwide, the numbers soar into the hundreds of millions.
The impact of diabetes extends far beyond the individual; it strains healthcare systems, impacts families, and reduces the quality of life for countless individuals. Managing diabetes effectively is not just about controlling blood sugar levels; it's about preventing the potentially devastating complications associated with the disease. These complications include cardiovascular disease, which remains the leading cause of death among diabetic patients, as well as kidney damage, vision loss, and nerve damage, which can lead to a range of further health issues.
Understanding the complexities of diabetes is the first step toward empowerment. By recognizing the symptoms and learning about the risk factors, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition effectively. In this article, we'll explore how integrating a holistic approach involving exercise, nutrition, and stress management can manage and improve your life with diabetes. This understanding and management are crucial in mitigating the fear and frustration that often accompany this diagnosis, providing a pathway to a healthier and more fulfilling life.
Join us as we delve deeper into the essential knowledge needed to tackle diabetes effectively, laying the groundwork for the comprehensive strategies discussed in the following sections.
Understanding Diabetes
Definition and Types
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high levels of glucose in the blood due to the body's inability to produce or properly use insulin. Diabetes is categorized into several types:
- Type 1 Diabetes: This form of diabetes affects about 1.6 million Americans, including 187,000 children and adolescents. It's an autoimmune condition in which the body attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The most common type, impacting around 34.1 million Americans. It typically develops in adulthood but is increasingly diagnosed in children and teens due to rising obesity rates.
- Gestational Diabetes: Occurs during pregnancy and affects up to 10% of pregnancies in the U.S. each year. It usually resolves after childbirth but increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Risk Factors
Diabetes development is influenced by a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors:
- Genetics: A family history of diabetes can increase susceptibility, especially for type 1 diabetes.
- Lifestyle Choices: Obesity, physical inactivity, and poor diet are significant risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain viruses is speculated to trigger type 1 diabetes.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Common symptoms include frequent urination, excessive thirst, fatigue, blurred vision, and sudden weight loss (particularly in type 1 diabetes). Diabetes is diagnosed through several tests:
- Fasting Plasma Glucose Test: Measures blood glucose after an overnight fast.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: Blood sugar is tested two hours after a sugary drink.
- HbA1c Test: Shows average blood sugar levels over the past three months.
By understanding these aspects, individuals can better manage their condition and prevent the onset of severe complications associated with diabetes.

The Role of Exercise in Diabetes Management
Exercise Recommendations
The American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) provides specific exercise guidelines for individuals with diabetes to help manage their condition effectively and enhance overall health. Here are the key recommendations:
- Aerobic Exercise: ACSM recommends that individuals with diabetes engage in at least 150 minutes per week of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes per week of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise. These exercises should be done at least three days per week, with no more than two consecutive days without exercise. Aerobic activities could include walking, cycling, swimming, or group fitness classes.
- Resistance Training: Resistance training should be performed at least twice weekly on non-consecutive days. This training should involve major muscle groups, utilizing exercises that include free weights, weight machines, resistance bands, or body-weight resistance (e.g., push-ups, squats).
- Flexibility and Balance: While not explicitly quantified like aerobic and resistance exercises, incorporating flexibility and balance exercises, such as yoga or Tai Chi, is also recommended. These activities improve joint range of motion, reduce the risk of injury, and enhance overall physical function.
These exercise prescriptions aim to improve glycemic control, assist in weight management, and reduce the risk of heart disease, which is particularly important given the increased cardiovascular risk associated with diabetes. Regular physical activity is crucial for effective diabetes management and enhancing the quality of life for those with the condition.
Impact of Exercise on Diabetes
Regular exercise plays a crucial role in managing diabetes due to its multiple benefits:
- Improves Blood Glucose Control: Exercise helps lower blood glucose levels and improves insulin sensitivity, which is essential for managing Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
- Reduces Cardiovascular Risk: Since diabetes increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, regular activity helps mitigate this risk by improving heart health and circulation.
- Aids in Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for people with Type 2 diabetes. Exercise helps with weight control by burning calories and increasing muscle mass, which boosts the body's metabolic rate.
- Enhances Overall Well-being: Regular physical activity can also help reduce stress, improve mood, and enhance overall quality of life, which is significant given the emotional challenges accompanying a diabetes diagnosis.
Tailoring Exercise to Individual Needs
Individuals with diabetes must tailor their exercise regimen based on their specific health status and reactions to different activities. Monitoring blood glucose levels before, during, and after exercise is crucial to ensure safety and to adjust the exercise plan as needed.
This section of our guide underscores the transformative power of exercise in managing diabetes, detailing practical steps to integrate physical activity into daily life for better health outcomes.
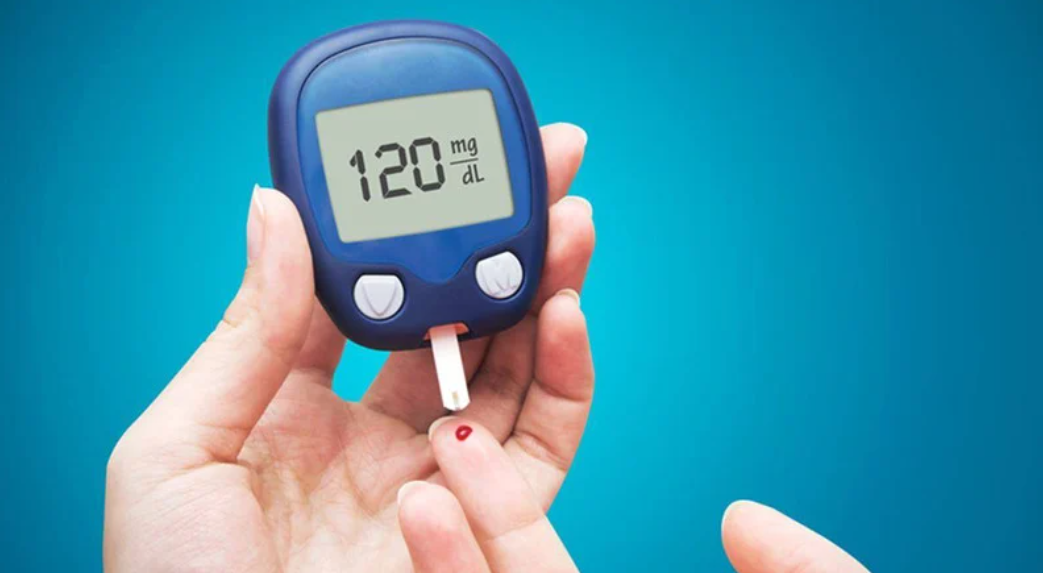

Things to Consider when Exercising with Diabetes
Exercising with diabetes is highly beneficial but requires careful planning and consideration to ensure safety and effectiveness. Here are some key things to consider and be cautious of when incorporating exercise into a diabetes management plan:
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Check blood glucose levels before, during, and after exercise to prevent sudden drops or spikes. Understanding how your body reacts to different activities will help you adjust your insulin doses and food intake to maintain safe glucose levels.
- Hydration: Keep hydrated before, during, and after exercise, as dehydration can affect blood sugar levels.
- Timing of Meals and Medications: Timing is crucial, especially if you are on insulin or other medications that lower blood sugar. It's important to ensure you have enough fuel for your activities and are not at risk of hypoglycemia. Eating a small carbohydrate-rich snack before exercising can help prevent low blood sugars during the workout.
- Type of Activity: Start with low to moderate-intensity activities and gradually increase intensity. Monitor how different activities affect your blood sugar and adjust accordingly. Aerobic exercises are generally recommended, but resistance training can also be beneficial in managing blood glucose levels.
- Duration and Frequency: Consistency is key in managing diabetes. Exercise for at least 150 minutes per week spread over several days. Avoid long periods without physical activity to help regulate blood sugar levels more effectively.
- Wear Appropriate Footwear: Foot care is crucial for people with diabetes due to the risk of neuropathy and poor circulation. Wear well-fitting, appropriate shoes, and inspect your feet daily for blisters, cuts, or sores.
- Emergency Snacks: Always have a fast-acting carbohydrate source with you in case of hypoglycemia. Examples include glucose tablets, juice, or regular soda.
- Adjustments for Weather Conditions: Exercise can be more challenging in extreme heat or cold, impacting blood sugar levels. Plan indoor activities when the weather is not conducive to outdoor exercise.
- Communication: Let someone know when and where you're exercising and understand the signs of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. Have a plan in place in case you need assistance.
- Medical Clearance: Before starting any new exercise program, consult with your healthcare provider, particularly if you have complications or concerns related to your diabetes.
By considering these factors, individuals with diabetes can safely enjoy the benefits of exercise and significantly enhance their overall health and well-being.
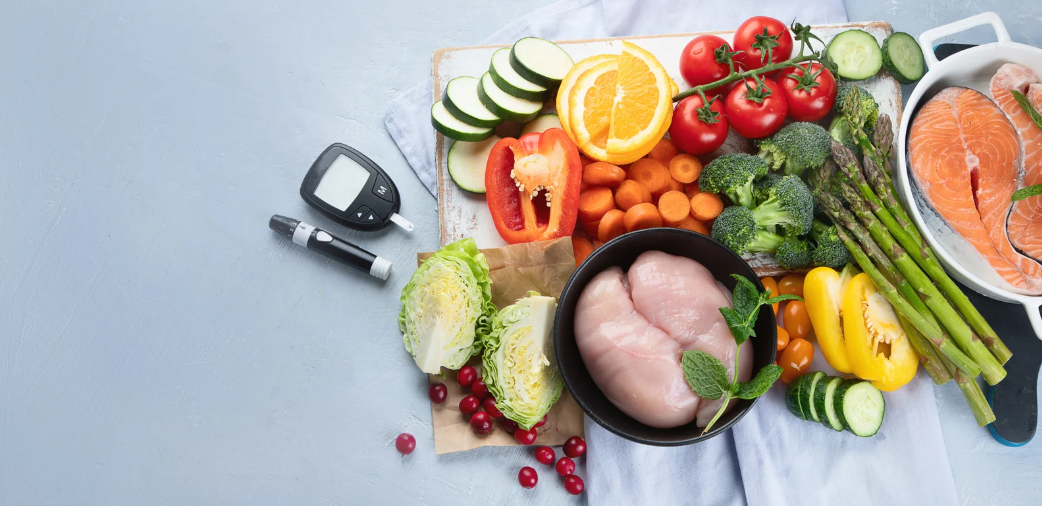

Nutritional Strategies for Managing Diabetes
Healthy Eating Patterns
Managing diabetes requires a thoughtful approach to nutrition, focusing on a balanced diet that supports stable blood sugar levels. A well-rounded diet for diabetes includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods that help maintain energy levels and optimize overall health.
- Complex Carbohydrates: Choose whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat products over refined grains. These foods have a lower glycemic index and provide a steady release of energy without causing sharp spikes in blood sugar.
- High-Fiber Foods: Fiber aids in blood sugar control by slowing the absorption of sugar. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains.
- Lean Proteins: Incorporate lean protein sources, such as chicken, turkey, fish, legumes, and tofu, which do not affect blood glucose levels and are essential for muscle repair and growth.
- Healthy Fats: Fats do not directly raise blood glucose and are vital for overall health. Opt for sources of unsaturated fats such as nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil.
Understanding the Glycemic Index
The glycemic index (GI) is a valuable tool for managing diabetes, as it ranks carbohydrates on a scale from 0 to 100 based on how quickly they raise blood glucose levels after eating:
- Low GI Foods (55 or less): Examples include sweet potatoes, most fruits, oatmeal, and legumes. These foods cause a gradual increase in blood sugar.
- Medium GI Foods (56-69): Foods like whole wheat products and brown rice fall into this category.
- High GI Foods (70 or above): These include white bread, white rice, and sugary cereals, which can cause quick spikes in blood glucose.
Incorporating more low-GI foods into your diet can help manage glucose levels more effectively, reducing the risk of spikes that complicate diabetes management.
Dietary Recommendations and Hormonal Considerations
Diabetes affects the body's ability to produce or respond to insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar. In individuals with type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to insulin, often exacerbated by excessive body weight and poor dietary choices. Managing dietary intake can significantly influence insulin sensitivity and overall hormonal balance.
- Reduce Sugar Intake: Limit foods and beverages high in added sugars, which can lead to significant insulin spikes and contribute to insulin resistance.
- Regular Meal Timing: Eating at regular intervals helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and improves insulin sensitivity. Avoid skipping meals, especially if you are on medications or insulin.
Navigating Diabetes with Diet
Understanding how foods affect blood sugar and insulin can empower those with diabetes to make informed choices that enhance their health without sacrificing the enjoyment of food. Implementing these nutritional strategies can help manage blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
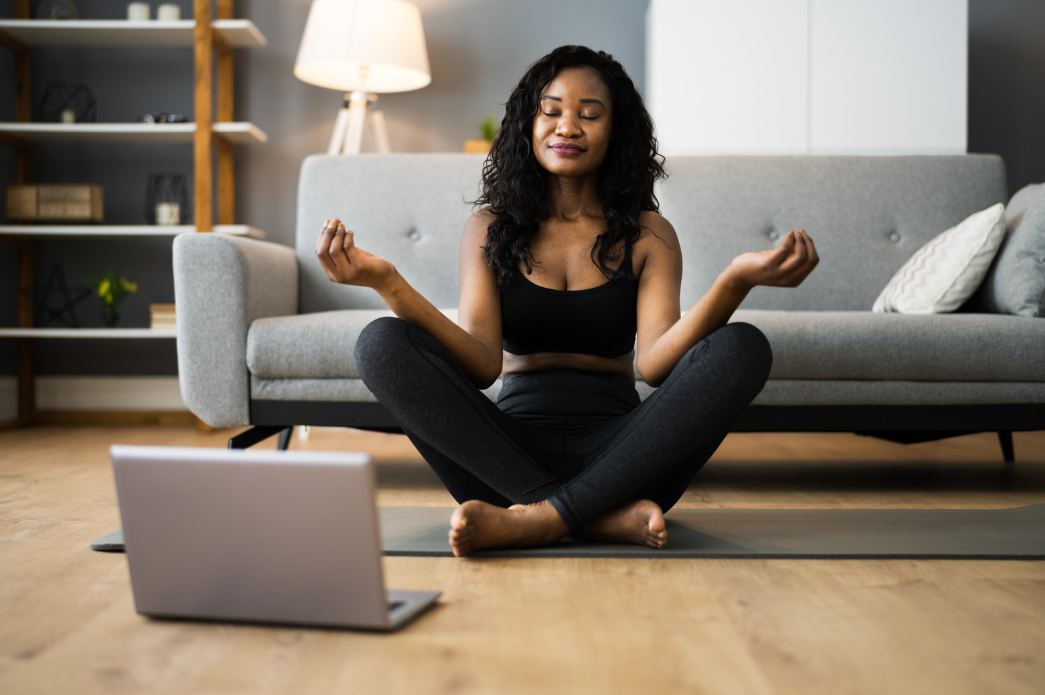

The Influence of Stress Management on Diabetes
Understanding the Connection
Stress plays a significant role in the management of diabetes, affecting blood glucose levels in both direct and indirect ways. When you're stressed, the body responds by releasing hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones can cause blood sugar levels to rise. For those with diabetes, the body's ability to manage this increase in glucose is compromised, which can lead to significant fluctuations in blood sugar levels. Additionally, stress can influence behavior, leading to poor dietary choices, reduced exercise, and inadequate sleep—all of which can adversely affect blood sugar control.
Stress Reduction Techniques
Effectively managing stress is a critical component of diabetes care. Here are several effective methods to reduce stress and help manage diabetes symptoms:
- Regular Physical Activity: Exercise is a natural stress reliever. Activities like walking, yoga, or swimming can help lower stress levels and positively affect blood sugar control.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practices such as mindfulness meditation can decrease stress and improve your reaction to stressful situations, helping to stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensuring sufficient sleep each night can help reduce stress and improve overall health. Sleep deprivation can increase stress and negatively impact blood glucose control.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Simple breathing techniques can help lower stress on the spot. Techniques like diaphragmatic breathing, where you focus on deep, even breaths, can help calm the mind and reduce stress.
- Professional Support: Counseling or therapy can be beneficial in managing chronic stress. A mental health professional can help develop strategies to manage stress effectively, which is particularly important for those dealing with the emotional challenges of diabetes.
By incorporating these stress reduction techniques into your daily routine, you can better manage your diabetes and improve your overall quality of life. Reducing stress not only helps control blood glucose levels but also addresses the broader emotional and psychological challenges associated with living with diabetes.

Royal Blue Fitness's Holistic Approach to Diabetes Management
Comprehensive Diabetes Management Program
At Royal Blue Fitness, we recognize the complexities of managing diabetes. We are committed to supporting our clients throughout their health journey. Our comprehensive diabetes management program is designed to address all aspects of diabetes care, encompassing customized exercise plans, dietary guidance, and effective stress management techniques.
- Customized Exercise Plans: We create personalized workout routines that cater to the unique needs of individuals with diabetes. Our plans emphasize a combination of aerobic, resistance, and flexibility exercises to improve blood sugar control, enhance cardiovascular health, and increase overall physical strength and mobility.
- Dietary Guidance: Nutrition plays a critical role in managing diabetes. Our nutrition experts work with clients to develop meal plans that balance blood sugar levels, incorporate nutrient-rich foods, and avoid high glycemic index ingredients. We provide practical advice on how to make informed food choices that support diabetes management and overall health.
- Stress Management Techniques: Understanding the link between stress and blood glucose levels, we offer strategies to manage stress effectively. This includes teaching relaxation techniques and mindfulness meditation and providing access to professional counseling if needed.
Success Stories and Testimonials
Our holistic approach has empowered many clients to take control of their diabetes and significantly improve their quality of life. Here are a few success stories from our community, but with different names to conceal their actual identity and respect their privacy:
- John's Journey: After being diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, John felt overwhelmed by the lifestyle changes he needed to make. Through our tailored exercise program and dietary adjustments, he has successfully reduced his HbA1c from 8.5% to 6.3% within six months. John now enjoys a more active lifestyle and better understands how to manage his condition.
- Emma's Experience: Emma struggled with gestational diabetes during her pregnancy and wanted to ensure it did not progress to type 2 diabetes postpartum. With our guidance, she adopted a fitness routine and dietary habits that helped her maintain a healthy weight and check her blood sugar levels. Emma's commitment to her health has paid off, and she continues to thrive.
These stories exemplify the effectiveness of our holistic approach and its positive impact on managing diabetes. At Royal Blue Fitness, we are dedicated to providing the support and resources our clients need to manage their diabetes confidently and live healthier lives.

Conclusion: Empowering Your Diabetes Journey
As we conclude this comprehensive guide, it's clear that managing diabetes is not merely about monitoring blood sugar levels—it's about embracing a holistic lifestyle that addresses all facets of health. Understanding the complexities of diabetes and the crucial role of diet, exercise, and stress management provides a strong foundation for effective disease management.
At Royal Blue Fitness, we are committed to empowering you on your journey to better health. By integrating tailored exercise programs, nutritional guidance, and stress management techniques, we help you navigate the challenges of diabetes with confidence. Our approach enhances your physical, mental, and emotional well-being, providing the tools to lead a more balanced and fulfilling life.
Taking proactive steps toward managing diabetes can dramatically improve your quality of life. It's about making consistent, informed choices that support your health goals. We invite you to take charge of your health, use the strategies outlined in this article, and consider joining Royal Blue Fitness for personalized support and guidance.
Resources for Managing Diabetes
For further information, guidance, and support on managing diabetes, consider exploring these resources from reputable organizations:
- American Diabetes Association (ADA): Offers comprehensive information on diabetes care, management, and education. This resource is invaluable for detailed guidelines on nutrition, exercise, and diabetes care practices. Visit ADA
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Provides extensive data on diabetes statistics, prevention tips, and management strategies. It's a great resource for learning about the impact of diabetes in the U.S. and effective prevention strategies. Visit CDC
- American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM): Offers guidelines on physical activity for individuals with diabetes. It's an essential resource for understanding the exercise recommendations specifically tailored to those managing diabetes. Visit ACSM
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK): Part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, NIDDK provides science-based information on diabetes management, including meal planning and the importance of physical activity. Visit NIDDK
- American Heart Association (AHA): Since diabetes significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases, AHA provides resources on how to manage heart health, which is crucial for individuals with diabetes. Visit AHA
- Mindful: This resource offers techniques and programs for stress management, which can be particularly beneficial for managing the mental health aspects of living with diabetes. Visit Mindful
These resources offer reliable and up-to-date information to help you understand more about diabetes, how to manage it effectively, and how to incorporate healthy lifestyle changes that can significantly improve your quality of life.

Subscribe to Our Newsletter and posts